Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 FCC hierarchical martensite transformation under dynamic impact in FeMnAlNiTi alloy
FCC hierarchical martensite transformation under dynamic impact in FeMnAlNiTi alloyLi, C.*; Fang, W.*; Yu, H. Y.*; Peng, T.*; Yao, Z. T.*; Liu, W. G.*; Zhang, X.*; 徐 平光; Yin, F.*
Materials Science & Engineering A, 892, p.146096_1 - 146096_11, 2024/02
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.02(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)The quasi-static superelastic responses and hierarchical martensite transformation from body-centered cubic (BCC) to face-centered cubic (FCC) under dynamic impact in Fe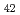 Mn
Mn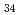 Al
Al Ni
Ni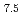 Ti
Ti alloys were investigated. Polycrystalline and oligocrystalline alloys were produced through solution heat treatment and cyclic heat treatment processes, respectively. The results show the volume fraction of residual martensite for oligocrystalline alloys is lower, which exhibits better superelastic responses compared with polycrystalline alloys. Dynamic impact tests indicate that, despite the weakening of the grain boundary strengthening effect, the ultimate strength of the oligocrystalline alloys closely matches that of the polycrystalline alloys under dynamic impact. The martensite transformation of the FeMnAlNiTi alloy is characterized as hierarchical under dynamic impact, and increasing strain rates and grain sizes can enhance the BCC
alloys were investigated. Polycrystalline and oligocrystalline alloys were produced through solution heat treatment and cyclic heat treatment processes, respectively. The results show the volume fraction of residual martensite for oligocrystalline alloys is lower, which exhibits better superelastic responses compared with polycrystalline alloys. Dynamic impact tests indicate that, despite the weakening of the grain boundary strengthening effect, the ultimate strength of the oligocrystalline alloys closely matches that of the polycrystalline alloys under dynamic impact. The martensite transformation of the FeMnAlNiTi alloy is characterized as hierarchical under dynamic impact, and increasing strain rates and grain sizes can enhance the BCC  FCC martensite transformation, resulting in higher martensite phase fractions for oligocrystalline alloys. The increase in ultimate strength is attributed to the dynamic Hall-Petch effect introduced by more martensite phase interfaces under dynamic impact.
FCC martensite transformation, resulting in higher martensite phase fractions for oligocrystalline alloys. The increase in ultimate strength is attributed to the dynamic Hall-Petch effect introduced by more martensite phase interfaces under dynamic impact.
 MnGaメタ磁性形状記憶合金の開発
MnGaメタ磁性形状記憶合金の開発伊東 達矢; Xu, X.*; 大森 俊洋*; 貝沼 亮介*
物性研だより, 63(3), p.8 - 10, 2023/10
メタ磁性形状記憶合金は磁場により駆動することが出来る形状記憶合金であり、センサーやアクチュエーター等での応用が期待されている。しかし、これまでに開発されてきた合金系ではマルテンサイト変態に伴うエネルギーロスが大きいという問題点があった。近年、我々の研究グループではPd MnGa合金において初めて相変態によるエネルギーロスの小さなメタ磁性形状記憶合金を発見した。本稿ではその内容を紹介する。
MnGa合金において初めて相変態によるエネルギーロスの小さなメタ磁性形状記憶合金を発見した。本稿ではその内容を紹介する。
Xu, X.*; 大平 拓実*; Xu, S.*; 平田 研二*; 大森 俊洋*; 植木 洸輔*; 上田 恭介*; 成島 尚之*; 長迫 実*; 貝沼 亮介*; et al.
Advanced Materials & Processes, 180(7), p.35 - 37, 2022/10
Metallic biomaterials are widely used to replace or support failing hard tissues due to excellent mechanical properties and high wear resistance, with demand increasing as the global population continues to age. It is widely accepted that successful metallic biomaterials should have good biocompatibility, high corrosion resistance, and strong wear resistance. In addition, a low Young's modulus similar to human bone is now recognized as another important factor, in order to avoid bone atrophy due to the stress shielding effect. While the Young's modulus of stainless steels and conventional fcc CoCr alloys is as high as 190-240 GPa, for  -type Ti-base alloys it is generally in the range of 50-80 GPa. Young's modulus values are as low as 35 GPa for Ti-Nb-Ta-Zr, close to that of human bone at approximately 10-30 GPa. However, Ti-base alloys come with the compromise of low wear resistance. In fact, alloys that feature a low Young's modulus along with high wear resistance have been difficult to realize. This article explores the recently developed bcc CoCr-base alloy Co-Cr-Al-Si as a potential solution to these issues, i.e., the difficulty in combining a low Young's modulus with high wear resistance, and the challenge of realizing large superelastic strains.
-type Ti-base alloys it is generally in the range of 50-80 GPa. Young's modulus values are as low as 35 GPa for Ti-Nb-Ta-Zr, close to that of human bone at approximately 10-30 GPa. However, Ti-base alloys come with the compromise of low wear resistance. In fact, alloys that feature a low Young's modulus along with high wear resistance have been difficult to realize. This article explores the recently developed bcc CoCr-base alloy Co-Cr-Al-Si as a potential solution to these issues, i.e., the difficulty in combining a low Young's modulus with high wear resistance, and the challenge of realizing large superelastic strains.
大平 拓実*; Xu, S.*; 平田 研二*; Xu, X.*; 大森 俊洋*; 植木 洸輔*; 上田 恭介*; 成島 尚之*; 長迫 実*; Harjo, S.; et al.
Advanced Materials, 34(27), p.2202305_1 - 2202305_11, 2022/07
被引用回数:12 パーセンタイル:87.92(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)The demand for biomaterials has been increasing along with the increase in the population of elderly people worldwide. The mechanical properties and high wear resistance of metallic biomaterials makes them well-suited for use as substitutes or as support for damaged hard tissues. However, unless these biomaterials also have a low Young's modulus similar to that of human bones, bone atrophy inevitably occurs. Because a low Young's modulus is typically associated with poor wear resistance, it is difficult to realize a low Young's modulus and high wear resistance simultaneously. Also, the superelastic property of shape memory alloys makes them suitable for biomedical applications, like vascular stents and guide wires. However, due to the low recoverable strain of conventional biocompatible shape memory alloys, the demand for a new alloy system is high. The novel body-center-cubic cobalt-chromium-based alloys in this paper provide a solution to both of these problems. We believe our novel alloys are promising candidates for biomedical applications.
Ahadi, A.*; 川崎 卓郎; Harjo, S.; Ko, W.-S.*; Sun, Q. P.*; 土谷 浩一*
Acta Materialia, 165, p.109 - 117, 2019/02
被引用回数:53 パーセンタイル:95.19(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We report emergence of an unprecedented elastocaloric effect with a decrease of temperature, well below the temperature range of martensitic phase transformation, in a model nanocrystalline NiTi that preserves slim-hysteresis superelasticity at ultra-low temperatures. The new elastocaloric effect emerges at a temperature of about 90 K, exhibits an opposite sign than the conventional elastocaloric effect, and intensifies gradually with a decrease of temperature to 18 K. At 18 K, a large adiabatic temperature change of +3.4 K is measured upon rapid release of tensile stress. The measured adiabatic temperature change are larger and extend over a wider temperature span than the existing electrocaloric, piezocaloric, and barocaloric cryo-refrigeration materials.
星屋 泰二
科学と工業, 75(8), p.379 - 387, 2001/08
Ti-Pd系の高温作動型形状記憶合金は、Ti-Ni系の形状記憶合金よりも遥かに高い変態温度(550~800K)を有することから原子力関連機器及び化学工学等、さまざまな応用分野への適用が検討されている。しかしながら、使用温度が高いことにより高温すべり変形が容易に導入されるため高温の変形挙動を正しく評価できないことが、同合金の実用化の進展を阻害する一因になっている。本稿では、TiPd-X(X=Cr, Fe)合金の高温変形挙動について着目し、降伏応力や回復歪の温度依存性について概説した。さらに、中性子照射挙動について検討し、TiPd-3Cr,TiPd-4Cr合金及びTiPd-6Fe,TiPd-7Fe合金の耐照射特性が良好であることを示した。
江草 茂則; 藤村 卓
インテリジェント・マテリアル, p.195 - 206, 1991/00
次世代の材料として期待されているインテリジェント材料(環境条件に知的に応答し、機能を発現する能力を有する新物質・材料)の応用分野の一つとして原子力や航空宇宙等の極限環境分野を取り上げ、将来この分野で使用されるインテリジェント材料を開発するための基盤技術の現状と発展の方向性について概説した。先端高分子複合材料等の母材中に圧電材料、形状記憶合金、光ファイバ、電気粘性流体等の機能性材料を埋め込み一体化することにより、センサ機能とアクチュエータ機能とを有するスマート材料を創製しようとする研究の幾つかを紹介する。現時点におけるこれらのスマート材料は、厳密な意味ではインテリジェント材料ではないが、将来インテリジェント材料に発展しうる有力候補の一つである。


 Al
Al


 Ni
Ni

 related to martensitic phase transition
related to martensitic phase transition森井 幸生; 飯泉 仁
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 54(8), p.2948 - 2954, 1985/00
被引用回数:41 パーセンタイル:88.04(Physics, Multidisciplinary)
 相Cu
相Cu


 Al
Al


 Ni
Ni

 の[110]横波(е
の[110]横波(е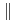 [110])フォノン分散関係を261,295,372Kで中性子散乱実験により測定した。このフォノン分枝は他に比べてエネルギーが極端に小さく、かつq=(2/3)qmaxの位置に「くぼみ」を持つという異常性を有している。この異常性を反映して(110)面間力のうち第2,第3近接面間力の効果が大きくなってきていることが明らかになった。さらに[110]軸に沿って存在する弾性散乱ピークには、温度依存性の異なる2種類のものが存在する事も判明した。こうした事実より、
[110])フォノン分散関係を261,295,372Kで中性子散乱実験により測定した。このフォノン分枝は他に比べてエネルギーが極端に小さく、かつq=(2/3)qmaxの位置に「くぼみ」を持つという異常性を有している。この異常性を反映して(110)面間力のうち第2,第3近接面間力の効果が大きくなってきていることが明らかになった。さらに[110]軸に沿って存在する弾性散乱ピークには、温度依存性の異なる2種類のものが存在する事も判明した。こうした事実より、
 相では2H型と18R型のマルテンサイトへ転移しようとする格子不安定性が2種類同時に存在して、それらが互いに競争して発展消滅を行っていると解釈できる。
相では2H型と18R型のマルテンサイトへ転移しようとする格子不安定性が2種類同時に存在して、それらが互いに競争して発展消滅を行っていると解釈できる。